How Can We Help?
-
Centro de unhas
-
- Linhas de Beau's
- Calos e calosidades
- Cloroníquia
- Dermatite
- Fungos dermatófitos e não dermatófitos
- Diabetes
- Erythronychia
- Hábitos
- Hangnails
- Hapaloníquia
- Distrofia da unha mediana de Heller'
- Hiperidrose
- Introdução às condições das unhas
- Koilonychia
- Distrofia lamelar
- Leuconíquia
- Melanoníquia
- Roer as unhas
- Clube das Unhas
- Ranhuras / depressões nos pregos
- Nail Pterygium
- Onicocriptose
- Onicólise
- Onychomadesis
- Onicomicose
- Onychophagia
- Onychotillomania
- Paroníquia
- Psoríase
- Hemorragias por estilhaços
- Onicomicose superficial branca
- Show all articles (16) Artigos sobre colapso
-
Pergunte aos especialistas
-
- As lixas de unha de vidro são melhores?
- Os empurradores de cutícula de metal são seguros?
- Can I cut the keratinised proximal nail fold (KPNF)?
- Posso usar apenas acetona para limpar a placa ungueal antes de um serviço?
- O esmalte de unha pode ser orgânico?
- Os produtos para unhas podem reparar a unha?
- A cutícula pode cobrir toda a unha?
- Você pode explicar os riscos negativos de lixar as paredes laterais da placa ungueal?
- Todas as placas ungueais crescem 1 mm por semana?
- As manicures estragam suas unhas?
- O lixamento das laterais da unha natural a enfraquece?
- O esmalte de unha ou o esmalte de gel UV desidrata a unha?
- A direção do lixamento das unhas é importante?
- A placa ungueal absorve algum produto químico encontrado nos produtos que usamos?
- Unhas encravadas. Qual'é o seu conselho?
- Como faço para salvar uma unha cortada?
- Como funcionam as gotas e sprays secantes de esmalte?
- Como o clima frio afeta as unhas?
- O cálcio é bom para as unhas?
- O cálcio é bom para a unha natural?
- O removedor de cutículas é indispensável?
- Meu esmalte é adequado para mim?
- É seguro usar esmalte de unha para uso repetitivo em clientes porque ele 'can't store pathogens'?
- Manchas de esmalte nas unhas
- Vitaminas pré-natais e crescimento das unhas
- Esmaltes de secagem rápida?
- Você deve lixar a unha natural antes de um revestimento de duas semanas?
- Alguns produtos para unhas afirmam que ajudam a placa ungueal a ficar mais forte. Essa afirmação é válida?
- O que são essas linhas pretas finas sob a unha?
- O que é uma manicure a seco?
- O que é uma manicure japonesa?
- O que é uma manicure úmida?
- Qual é o tipo mais seguro de manicure?
- Qual é o melhor tipo de manicure para se fazer?
- Qual é a diferença entre uma manicure francesa e uma manicure americana?
- Qual'o problema de deixar a água de molho?
- Qual é o problema com a granulação de uma lixa de unha?
- O que é melhor? Água e sabão ou desinfetante para as mãos antes de um serviço?
- Como limpar a poeira?
- Por que as camadas superiores de esmalte ficam pegajosas quando aplicadas?
- Por que devo usar uma base flexível?
- Show all articles (26) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- Primers à base de ácido ou sem ácido?
- As extensões de unhas de gel são melhores do que as de acrílico?
- Meus sistemas de unhas são porosos ou não?
- Posso fazer o e-file da unha natural embaixo de um aprimoramento?
- É possível misturar o líquido de um sistema com o pó de outro?
- Aprimoramentos de pó de imersão?
- Os acrílicos têm um futuro limitado?
- Existe um monômero universal?
- O esmalte em gel é inflamável?
- Qual a quantidade de produto a ser removida durante o rebalanceamento?
- O L&P é mais perigoso do que o gel?
- Existe um pó universal para unhas acrílicas que funcione com qualquer líquido monômero?
- Óleo para unhas e lifting
- Aprimoramentos de pinçamento?
- Algumas marcas lascam mais rápido do que outras. Isso é um problema do produto ou da química do corpo?
- O óleo da árvore do chá é absorvido pela unha?
- Para preencher ou absorver?
- Beliscar ou não o realce da unha?
- Entendendo a diferença entre a solução de deslizamento e o limpador para unhas de polímero
- O que faço com meu monômero restante?
- Qual é a diferença entre manicure francesa e rosa e branco?
- Qual é a diferença entre Fiber Base e Normal Base?
- Qual o tamanho do pincel a ser usado?
- Por que as unhas ficam finas após a remoção de um revestimento de unha?
- Show all articles (9) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- Uma queimadura química?
- Uso de autoclave
- Posso ter dor de cabeça ao trabalhar com produtos para unhas?
- Posso higienizar e desinfetar os separadores de dedos dos pés?
- Posso usar meu forno para esterilizar minhas ferramentas?
- Posso usar supercola em vez de resina para as extensões de unhas de fibra de vidro ou não funciona da mesma forma?
- Posso trabalhar com clientes diabéticos?
- Você pode explicar os riscos negativos de lixar as paredes laterais da placa ungueal?
- É possível misturar produtos Hema e Hema-Free?
- É possível higienizar ferramentas de metal com álcool isopropílico?
- Soluções desinfetantes e dispositivos ultrassônicos
- Preciso de qualificações para fazer unhas?
- Os dispositivos de saneamento UV funcionam?
- O óleo para cutículas realmente quebra a cola de unha tradicional?
- A direção do lixamento das unhas é importante?
- Aprimoramentos em Nail Biters?
- Escova felpuda ou sintética para tirar o pó
- Desinfetante para as mãos ou lavagem das mãos?
- Não tenho certeza de como trabalhar em unhas com Pterígio.
- É seguro usar um E-File?
- A Covid ou a higienização das mãos está afetando os serviços de unhas?
- O gel de cura sob unhas opacas é um perigo para as unhas?
- A lavagem das mãos está causando a elevação dos produtos para unhas?
- A higienização é suficiente?
- O material das luvas de látex é tal que causa sensibilidade nas mãos?
- Meu cliente tem lascas/perda de realce e eu nunca tive isso antes?
- Máscaras faciais para salão de beleza
- Grávida e pensando em fazer faculdade de tecnologia de unhas. Há alguma preocupação adicional além da ventilação e da higiene, ou devo adiar por enquanto?
- Deve-se usar uma máscara durante todo o serviço?
- Devo desinfetar todas as escovas de unha?
- Devo usar um "aglutinante de proteínas" para evitar a elevação?
- Você deve colocar o final de uma garrafa velha na nova?
- Alguns produtos para unhas afirmam que ajudam a placa ungueal a ficar mais forte. Essa afirmação é válida?
- Alguns de meus clientes estão tendo picos de calor ao curar a base e a camada superior.
- Gabinetes de luz UV para lixas de unha?
- O uso de protetor solar pode levar à interrupção do serviço?
- Quais são os requisitos legais para o tratamento de menores de idade?
- O que acontece quando a acetona é misturada com óleos?
- O que é uma manicure no estilo brasileiro?
- O que é uma manicure combinada?
- O que é uma manicure russa?
- Qual é a diferença entre limpeza, desinfecção e esterilização?
- Qual é a diferença entre HEMA e di-HEMA?
- Quando os esmaltes perdem a validade?
- Onde posso encontrar níveis seguros de ingredientes para gel e gel construtor?
- Why shouldn’t pumice stones be reused in pedicures?
- Show all articles (31) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- Acrilatos em esmaltes tipo gel?
- A acetona pode causar bolhas?
- Posso ter dor de cabeça ao trabalhar com produtos para unhas?
- Can long-wear nail polishes cause acrylate allergies like gel nails do?
- Meu cliente pode ser alérgico à acetona?
- Tenho uma alergia ou irritação?
- Produtos para unhas sem glúten?
- Como eu adquiri uma alergia ao gel?
- Como explico o fato de estar me tornando alérgico ao meu cliente que "sabe mais"?
- A acetona é segura para remover produtos para unhas?
- O BPMMA é seguro para pregos de pressão?
- É seguro aplicar um revestimento sobre o Onycholysis?
- O gel à base de borracha é mais propenso a fungos e infecções do que o gel normal?
- Existe uma manicure de gel segura?
- Pressão nas unhas, reação alérgica curada, posso tentar usar gel novamente?
- O óleo da árvore do chá é absorvido pela unha?
- O uso de protetor solar pode levar à interrupção do serviço?
- O que causa a reação da pele depois que o produto para unhas é removido?
- Quais marcas de gel UV você recomenda?
- Por que estamos vendo mais reações dos serviços de polimento com gel do que dos serviços de aprimoramento com gel?
- Show all articles (5) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- As extensões de unhas de gel são melhores do que as de acrílico?
- Os géis duros são para todos?
- Meus sistemas de unhas são porosos ou não?
- As unhas postiças são uma alternativa segura se você tiver uma reação alérgica ao gel?
- Os géis UV são melhores para as unhas?
- O acrílico pode ser usado sob pontas de cobertura total?
- Posso fazer o e-file da unha natural embaixo de um aprimoramento?
- É possível misturar produtos Hema e Hema-Free?
- As unhas de gel estragam suas unhas?
- Os pigmentos do esmalte em gel, por si só, explicam por que os profissionais de unhas o aplicam em uma camada fina em comparação com o gel construtor?
- A cura por congelamento interrompe o processo de cura?
- O uso de gel UV com pontas transparentes de cobertura total cura adequadamente?
- Gel nos dedos dos pés?
- Como posso encontrar uma linha de polimento em gel UV não tóxica?
- O esmalte em gel é inflamável?
- Qual a quantidade de produto a ser removida durante o rebalanceamento?
- Se eu usar uma lâmpada LED para unhas em um produto projetado para lâmpadas UV tradicionais, o gel UV ficará curado demais?
- Camada de inibição e géis sem limpeza
- A manicure com gel UV é segura para quem já teve problemas de saúde na pele?
- O gel de cura sob unhas opacas é um perigo para as unhas?
- O aquecimento do gel UV é um problema?
- É verdade que o gel de LED cura de baixo para cima?
- O L&P é mais perigoso do que o gel?
- O gel à base de borracha é mais propenso a fungos e infecções do que o gel normal?
- A base de borracha descascada é o mesmo que o revestimento de base de borracha?
- Existe uma manicure de gel segura?
- Sistemas de mistura de pregos
- Óleo para unhas e lifting
- Praticando em mim mesmo e de fácil remoção?
- Pressão nas unhas, reação alérgica curada, posso tentar usar gel novamente?
- Remoção de gel não curado
- Devo comprar minha lâmpada para unhas com base na potência?
- Devo fazer unhas de gel ou de imersão?
- Meus clientes devem lavar as mãos antes de eu aplicar o óleo?
- Os géis UV devem "queimar como loucos"?
- Devemos remover a base de borracha da placa ungueal?
- Algumas marcas lascam mais rápido do que outras. Isso é um problema do produto ou da química do corpo?
- Às vezes, as bordas livres ficam mais nítidas após a remoção do líquido?
- Para preencher ou absorver?
- Beliscar ou não o realce da unha?
- Entendendo a diferença entre a solução de deslizamento e o limpador para unhas de polímero
- Usar óleo para cutículas durante a remoção?
- GEL UV misturado com acrílicos - consultas de cura
- Diluente para polimento em gel UV
- O que causa a reação da pele depois que o produto para unhas é removido?
- O que realmente significa 'overcured'?
- Qual é o método correto para aplicar um produto do tipo 'BIAB'?
- Qual é a diferença entre manicure francesa e rosa e branco?
- Qual é a diferença entre Fiber Base e Normal Base?
- Qual é a diferença entre HEMA e di-HEMA?
- Que tipo de produtos são as resinas de envoltório e os géis sem luz?
- Quais marcas de gel UV você recomenda?
- Onde posso encontrar níveis seguros de ingredientes para gel e gel construtor?
- Por que estamos vendo mais reações dos serviços de polimento com gel do que dos serviços de aprimoramento com gel?
- Por que as unhas ficam finas após a remoção de um revestimento de unha?
- Por que algumas cores de gel UV desbotam?
- Por que você aconselha a limpeza de um produto sem limpeza para revestir?
- Uma lâmpada de mesa de LED afetará os géis curados com LED?
- Show all articles (43) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- As lâmpadas UV são seguras?
- Se eu usar uma lâmpada LED para unhas em um produto projetado para lâmpadas UV tradicionais, o gel UV ficará curado demais?
- Devo comprar minha lâmpada para unhas com base na potência?
- E quanto aos clientes com histórico de câncer de pele?
- O que realmente significa 'overcured'?
- Qual lâmpada UV para unhas devo usar?
-
- Um verde! Por quê? O que eu faço?
- A imersão em acetona pode alterar a estrutura das unhas?
- As unhas precisam respirar?
- A manicure causa distrofia mediana das unhas (solenoníquia)?
- A artrite ativa nos nós dos dedos afeta a placa ungueal com relação ao levantamento de peso?
- Como faço para evitar os "verdes"?
- Como faço para limpar a hiperqueratose do leito ungueal?
- Como tratar a "síndrome da unha verde"?
- Como o clima frio afeta as unhas?
- Não tenho certeza de como trabalhar em unhas com Pterígio.
- Tenho quase certeza de que minha cliente de manicure de gel UV tem WSO
- É seguro aplicar um revestimento sobre o Onycholysis?
- O material das luvas de látex é tal que causa sensibilidade nas mãos?
- Leuconíquia ou não?
- Líquen plano. O que devo fazer?
- Should you put gel polish on your skin to check for allergens?
- O óleo da árvore do chá é absorvido pela unha?
- O teste de onicomicose (unha com fungos) é positivo... E agora?
- Tratamento de unhas com fungos
- O que são essas linhas pretas finas sob a unha?
- O que é a onicólise?
- What is the best treatment for white keratin granulations on your toes?
- O que fazer com as unhas que não estão saudáveis?
- Manchas brancas nas unhas após a remoção do adesivo
- Por que há sulcos em minhas unhas?
- Why did my white tips turn yellow and dark right after they were put on?
- Why Do I Get Sinus Irritation at the Nail Salon?
- Por que a seda ou a fibra de vidro são boas para unhas mais finas, danificadas e fracas?
- Por que NÃO deveríamos cobrir os "verdes"?
- Show all articles (14) Artigos sobre colapso
-
- Aplicando aprimoramentos de unhas em crianças?
- Como faço para salvar uma unha cortada?
- Como posso trabalhar com um cliente com diabetes tipo 2?
- Sou autônomo e tenho um salão de beleza em casa. Preciso fazer uma avaliação de risco?
- A manicure com gel UV é segura para quem já teve problemas de saúde na pele?
- Grávida e pensando em fazer faculdade de tecnologia de unhas. Há alguma preocupação adicional além da ventilação e da higiene, ou devo adiar por enquanto?
- O médico diz "vá em frente". Devo fazê-lo?
- Quais são os requisitos legais para o tratamento de menores de idade?
-
- A imersão em acetona pode alterar a estrutura das unhas?
- Can I cut the keratinised proximal nail fold (KPNF)?
- A cliente não deixa ninguém polir as bordas de suas unhas?
- Todas as placas ungueais crescem 1 mm por semana?
- Crescimento do hiponíquio
- Quais são os selos da unidade de unha?
- Qual é a função da matriz de unhas?
- Qual é a diferença entre o leito ungueal e a placa ungueal?
- Como também é conhecida a matriz da unha?
- De onde vem o óleo da lâmina ungueal se o leito ungueal não tem glândulas?
- Onde está a cutícula?
- Por que as cutículas de minhas clientes ficam mais grossas durante o inverno?
-
- Posso usar supercola em vez de resina para as extensões de unhas de fibra de vidro ou não funciona da mesma forma?
- Can long-wear nail polishes cause acrylate allergies like gel nails do?
- Você sabe se deixar as unhas de molho em óleo de abacate morno pode manchar suas unhas de amarelo?
- Um gel que contém apenas metacrilato de benzila e etilenoglicol dimetacrilato pode ser considerado hipoalergênico?
- How does clear 3d sculpting gel work?
- Estou confuso com o termo polimento híbrido ou polimento híbrido em gel.
- O BPMMA é seguro para pregos de pressão?
- A cliente não deixa ninguém polir as bordas de suas unhas?
- As unhas precisam respirar?
- A placa ungueal absorve algum produto químico encontrado nos produtos que usamos?
- Aprimoramentos em Nail Biters?
- Como eu adquiri uma alergia ao gel?
- O esmalte em gel é inflamável?
- Os géis UV devem "queimar como loucos"?
- O óleo da árvore do chá é absorvido pela unha?
-
-
Suporte
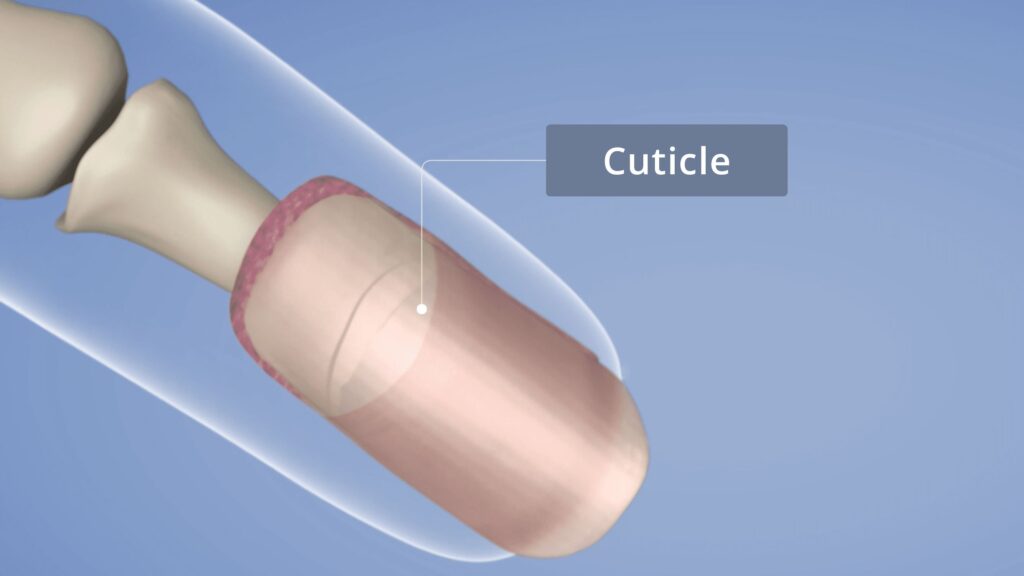
Cuticle
12.6k visualizações
Was this article helpful?
We'd love to hear your feedback:
The cuticle is created by the eponychium on the ventral (on underside) surface of the proximal nail fold. The cuticle is formed of sticky dead skin cells that are shed by the living skin of the PNF just like the skin cells are from any surface of epidermis but instead of falling off in flakes, they are bound together with a very sticky substance, that sticks them firmly to the emerging nail plate beneath them and the frame of keratinised epidermis above them. This important part of the nail seal (or guardian) at the base of the nail is curated by the eponychium which ‘sticks’ the dead skin cells together.
Essa fina camada de pele morta adere rapidamente à placa ungueal e à prega ungueal proximal, forming an important seal that protects the important matrix that is behind and below the PNF. This is non-living skin, though, and is safely removed prior to manicures and pedicures, to avoid any lifting of artificial nails, for example.
Pergunte aos especialistas
Você deve empurrar suas cutículas para trás?
The answer to this is NO! The cuticle that is exposed and on the nail plate can be safely removed as it is non-living tissue, however to prevent infection of the finger, stop when you reach the frame of keratinised epidermis at the edge of the proximal nail fold. If you go further, and push deep under the proximal nail fold, you open the area up to infection.
Na realidade, a cutícula precisa ser levantada da placa ungueal quando estiver amolecida e depois removida.
Qual é a função da cutícula?
With the proximal nail fold and the nail plate sealed together with the sticky cuticle in the middle, there is a very efficient first line of defense against all types of invaders from pathogens to chemicals to fungus spores. Any of these that reach the delicate matrix can very easily interrupt the growth of the nail plate and even stop growth altogether.
De que é feita a cutícula?
A cutícula é formada por células incolores e não vivas da pele.
Como você remove a cutícula?
Idealmente, antes de fazer qualquer coisa na cutícula da placa ungueal, ela precisa ser amolecida. Historicamente, isso tem sido feito por meio de deixar as unhas de molho em água amolecida. Isso amolecerá a cutícula de forma muito eficaz, MAS também criará um efeito indesejado na placa ungueal.
The nail plate is hydrophilic, meaning it loves water and is very porous due to the time air spaces within it. If it is soaked in water for 1 minute or more, it will allow water to penetrate the structure, change the shape, temporarily, and make it very soft until the excess water has evaporated. Then it will return to its original shape and regain its hardness.
If an overlay of any kind is applied to a ‘water logged’ nail plate there is a good chance of lifting when the nail returns to its original shape.
Os produtos e as técnicas modernas deixaram de usar a imersão em água e passaram a usar produtos muito mais eficientes para amolecer as cutículas.
These can be an alkaline based product such as sodium hydroxide. This is very efficient at breaking the bonds between dead skin cells and softening the layer. It should, however, NOT be left on the nail nor skin as it will continue to work and will also soften the nail plate and make it very susceptible to damage during the nail service. It needs to be neutralised by a mild solution of soapy water that can be applied via a water spray and drying with a disposable wipe or by washing the hands with liquid soap and running water.
Como alternativa, a aplicação de um bom óleo para unhas no início do serviço, mas depois que as unhas tiverem sido removidas e limpas. Isso pode amolecer com eficiência a pele morta da cutícula enquanto as unhas estão sendo modeladas. Em seguida, a pele amolecida pode ser removida com segurança por uma boa ferramenta de cutícula, tomando cuidado para não danificar a superfície da unha nem o PNF.
This process can also be safely achieved using an e-file. This technique needs education, a slow e-file speed, suitable e-file bit and, preferably oil to minimise any nail plate damage.
There are some e-file techniques that are very extreme in the removal of skin in this area. If you understand the structure and purpose of the PNF it is very clear that this area must be protected at all costs. The ‘seal’ must NOT be broken and therefor opening the matrix to pathogens.
Those nail pros and, indeed, respected educators, who carry out and teach the extreme version of this technique, clearly have no real understanding of the physiology and pathology of the area! (Maybe link to all or any of Vitaly or Doug’s articles on this topic)
Em conclusão:
- A cutícula é uma fina camada de pele morta na superfície da placa ungueal.
- Ela é criada pelo eponíquio na parte inferior da dobra ungueal proximal.
- The cuticle is the middle layer of the proximal nail fold and nail plate, and it forms a crucial seal at the base of the nail, safeguarding the delicate matrix.
- Ele pode ser removido com segurança e eficácia sem danificar a vedação.
- A remoção da cutícula é necessária para facilitar a adesão das sobreposições à placa ungueal e para obter uma borda limpa e organizada na sobreposição.
Galeria de imagens
Was this article helpful?
We'd love to hear your feedback:
