La banda onicodérmica
We see it every day while we’re at work, but do we really know what it is? Let’s take a closer look at Doug Schoon’s illustration to get a better understanding.
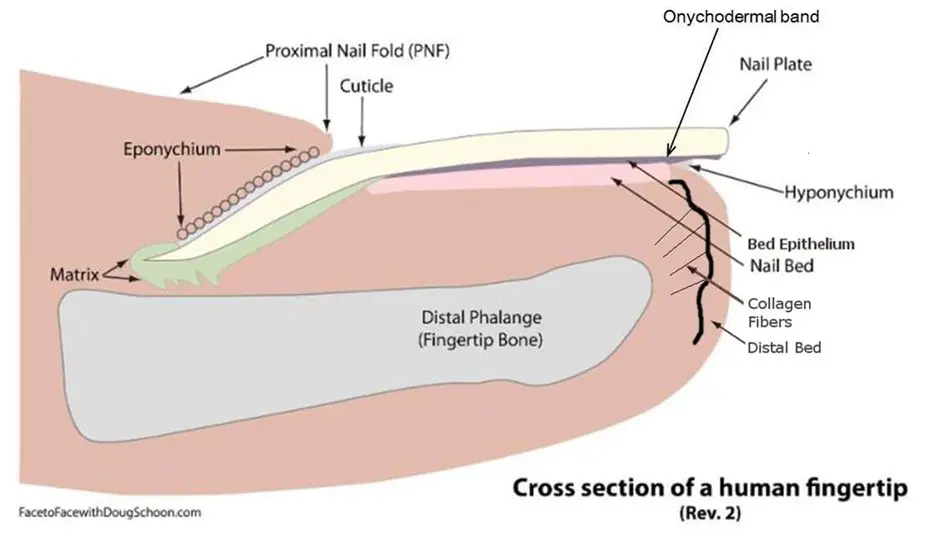
If we attempt to view it from behind the free edge, it appears like this:
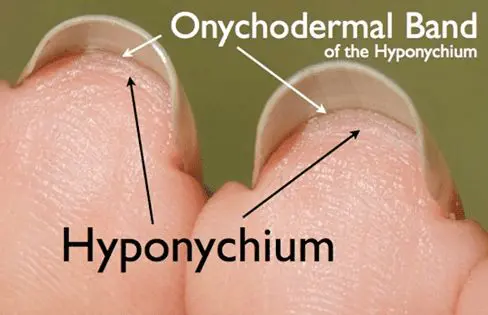
• The Onychodermal Band is non-living tissue. It’s an extension of the bed epithelium.
• It has a gray-brownish color.
La banda onicodérmica: Una barrera protectora oculta
Entre el placa para clavos and the nail bed lies the bed epithelium. When the bed epithelium reaches the end of the lecho ungueal y se pliega sobre sí misma, se convierte en la Banda Onicodérmica. Este tejido estrecho y compactado actúa como una barrera patógena adicional por debajo de la piel libre. borde de la lámina ungueal. Forma una asociación con la hiponiquio and together they become a super seal – it often goes unnoticed and is nearly invisible. You have to look closely to perceive it.
La banda onicodérmica es algo translúcida, una fina capa bajo el borde distal (borde libre) del placa para clavosque abarca toda la anchura de la lámina ungueal y bordea el blanco visible del borde libre.
La banda onicodérmica sirve para impedir que los organismos infecciosos y contaminantes más pequeños se infiltren en el lecho ungueal. Si se vulnera este tejido protector (barrera patógena), la uña la placa se separa del lecho ungueal causing onycholysis and dramatically increasing the risk of infection.
Its partner in the nail unit is the Hyponychium and that hyponychium is one of the four guardian seals of the nail unit, designed to protect the lecho ungueal from germs and other infections, such as fungus or yeast. While the hiponiquio is composed of living epidermal tissue. It’s important to note that the Onychodermal Band is non-living tissue and needs to remain elastic to perform its job effectively.
Mejorar la elasticidad: Aplicar aceite detrás del borde libre para la salud de las uñas
Aplicación de aceite detrás del borde libre, en lugar de encima de la placa ungueal, puede ayudar a mantener la elasticidad necesaria, incluso si la banda onicodérmica ya se ha desprendido.
Medidas de precaución y consideraciones autoinmunes para el cuidado de las uñas
Cuidado al utilizar un Efile para acortar la uña que sale de un mejora de las uñas behind the free edge or if you use a sharp instrument to clean under the free edge, might accidentally damage it, and you’ll immediately see the consequences as onycholysis.
Algunas enfermedades autoinmunes también pueden influir:
• Psoriasis
• Lichen Planus
• Eczema
Todas ellas son enfermedades que pueden afectar a la banda onicodérmica, la matriz ungueal, la lámina ungueal o el lecho ungueal, lo que provoca la rotura del sello. La aplicación de aceite detrás del borde libre es crucial porque el aceite repele el agua, mantiene el sello guardián elástico y no proporciona una fuente de nutrición para los gérmenes, ofreciendo una excelente protección.
In this image, you can clearly see how psoriasis can affect it. When the ‘oil slick’ blister forms, the bed epithelium is directly affected by the upwards pressure of the blister dislodging it from the nail bed. As the nail plate moves (perpetual motion) and the damaged bed epithelium gets closer to the free edge onycholysis is a fact and the nail bed is exposed to any and all pathogens.
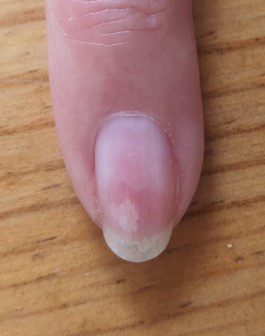
Sometimes, you may also notice that the hyponychium is pulled along with the Onychodermal Band. Something simple (but not always noticed) like product shrinkage can easily cause this to happen. If you recognize this happening, stop with your nail product until the hyponychium is recovered or find a more flexible product. Here, too, a good quality oil is your friend. If you work with a cuticle pusher or an e-file in this area, you’re likely to cause more irritation.
The Onychodermal Band is of utmost importance for the overall health of the nail unit and must be treated with care. Being cautious during cleaning under the free edge is necessary. It’s better to clean with a soft brush and oil, always avoiding sharp objects under the free edge to keep the nail unit healthy.
En conclusión
The Onychodermal Band may go unnoticed in our daily lives, but it plays a crucial role in protecting our nails from infections and maintaining their overall health. Understanding its function and how to care for it is essential for nail health and hygiene. So, next time you’re working on your nails, remember the significance of the Onychodermal Band and treat it with the care it deserves to keep your nails looking and feeling their best.


