How Can We Help?
-
Centro de uñas
-
- Líneas de Beau's
- Callos y durezas
- Cloroniquia
- Dermatitis
- Hongos dermatofitos y no dermatofitos
- Diabetes
- Erythronychia
- Hábitos
- Uñeros
- Hapaloniquia
- Distrofia ungueal media de Heller's
- Hiperhidrosis
- Introducción a las afecciones de las uñas
- Koilonychia
- Distrofia laminar
- Leuconiquia
- Melanoniquia
- Morderse las uñas
- Club de uñas
- Ranuras / Depresiones para clavos
- Nail Pterygium
- Onicocriptosis
- Onicólisis
- Onychomadesis
- Onicomicosis
- Onychophagia
- Onychotillomania
- Paroniquia
- Psoriasis
- Hemorragias en astilla
- Onicomicosis superficial blanca
- Show all articles (16) Colapsar artículos
-
Pregunte a los expertos
-
- ¿Son mejores las limas de cristal?
- ¿Son seguros los empujadores de cutícula metálicos?
- Can I cut the keratinised proximal nail fold (KPNF)?
- ¿Puedo utilizar sólo acetona para limpiar la placa de la uña antes de un servicio?
- ¿Puede ser ecológico el esmalte de uñas?
- ¿Pueden los productos para uñas reparar la uña?
- ¿Puede la cutícula cubrir toda la uña?
- ¿Puede explicar los riesgos de limar las paredes laterales de la placa ungueal?
- ¿Crecen todas las placas ungueales 1 mm a la semana?
- ¿La manicura estropea las uñas?
- ¿El limado de los laterales de la uña natural la debilita?
- ¿El esmalte de uñas o el esmalte en gel UV deshidratan la uña?
- ¿Importa la dirección del limado de uñas?
- ¿La lámina ungueal absorbe las sustancias químicas de los productos que utilizamos?
- Los padrastros. ¿Cuál'es tu consejo?
- ¿Cómo puedo salvar una uña cortada?
- ¿Cómo funcionan las gotas y sprays secadores de esmalte de uñas?
- ¿Cómo afecta el frío a las uñas?
- ¿Es bueno el calcio para las uñas?
- ¿Es bueno el calcio para la uña natural?
- ¿Es imprescindible un quitacutículas?
- ¿Es adecuado para mí el esmalte de uñas?
- ¿Es seguro el esmalte de uñas para uso repetitivo en clientes porque 'no puede'almacenar patógenos'?
- Manchas de esmalte en las uñas
- Vitaminas prenatales y crecimiento de las uñas
- ¿Esmaltes de secado rápido?
- ¿Hay que limar la uña natural antes de un recubrimiento de dos semanas?
- Algunos productos para uñas afirman que ayudan a fortalecer la placa ungueal. ¿Es válida esta afirmación?
- ¿Qué son esas finas líneas negras bajo la uña?
- ¿Qué es la manicura en seco?
- ¿Qué es la manicura japonesa?
- ¿Qué es la manicura húmeda?
- ¿Cuál es el tipo de manicura más seguro?
- ¿Cuál es el mejor tipo de manicura?
- ¿Qué diferencia hay entre la manicura francesa y la americana?
- ¿Qué tiene de malo un baño de agua?
- ¿Qué pasa con el grano de una lima de uñas?
- ¿Qué es mejor? ¿Jabón y agua o desinfectante de manos antes de un servicio?
- ¿Por dónde se quita el polvo?
- ¿Por qué los esmaltes de uñas quedan fibrosos al aplicarlos?
- ¿Por qué utilizar una base flexible?
- Show all articles (26) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Imprimaciones ácidas o sin ácido?
- ¿Son mejores las extensiones de uñas de gel que las acrílicas?
- ¿Mis sistemas de uñas son porosos o no?
- ¿Puedo limar la uña natural debajo de una mejora?
- ¿Se puede mezclar líquido de un sistema con polvo de otro?
- ¿Mejoras del polvo de inmersión?
- ¿Tiene el acrílico un futuro limitado?
- ¿Existe un monómero universal?
- ¿Es inflamable el esmalte en gel?
- ¿Cuánto producto hay que retirar durante el reequilibrio?
- ¿Es L&P más peligroso que el gel?
- ¿Existe un polvo universal para uñas acrílicas que funcione con cualquier líquido monómero?
- Aceite y lifting para uñas
- ¿Pellizcando mejoras?
- Algunas marcas se astillan más rápido que otras, ¿es un problema del producto o de la química corporal?
- El aceite del árbol del té, ¿se absorbe a través de la uña?
- ¿Para rellenar o para empapar?
- ¿Pellizcar o no el realce de la uña?
- Comprender la diferencia entre solución deslizante y limpiador para uñas de poligel
- ¿Qué hago con el monómero que me sobra?
- ¿Qué diferencia hay entre la manicura francesa y la rosa y blanca?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la base de fibra y la base normal?
- ¿Qué tamaño de pincel utilizar?
- ¿Por qué se notan las uñas finas después de retirar el esmalte?
- Show all articles (9) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Una quemadura química?
- Uso del autoclave
- ¿Puedo tener dolor de cabeza por trabajar con productos para las uñas?
- ¿Puedo higienizar y desinfectar los separadores de dedos?
- ¿Puedo utilizar el horno para esterilizar mis herramientas?
- ¿Puedo utilizar superglue en lugar de resina para las extensiones de uñas de fibra de vidrio o no funciona igual?
- ¿Puedo trabajar con clientes diabéticos?
- ¿Puede explicar los riesgos de limar las paredes laterales de la placa ungueal?
- ¿Se pueden mezclar productos Hema y Hema-Free?
- ¿Se pueden desinfectar las herramientas metálicas en alcohol isopropílico?
- Soluciones desinfectantes y dispositivos ultrasónicos
- ¿Necesito titulación para hacer uñas?
- ¿Funcionan los dispositivos de saneamiento UV?
- ¿El aceite para cutículas descompone realmente el pegamento tradicional para uñas?
- ¿Importa la dirección del limado de uñas?
- ¿Mejoras en los mordedores de uñas?
- Cepillo de pelusa frente a cepillo sintético para quitar el polvo
- ¿Desinfectante o lavado de manos?
- No tengo claro cómo trabajar las uñas con Pterigión.
- ¿Es seguro utilizar un expediente electrónico?
- ¿Afecta Covid o la desinfección de manos a los servicios de uñas?
- ¿Es peligroso curar el gel bajo las uñas opacas?
- ¿Se levantan las uñas por lavarse las manos?
- ¿Es suficiente con desinfectar?
- ¿Es el material de los guantes de látex tal que provoca sensibilidad en las manos?
- Mi cliente tiene chipping/pérdida de realce y nunca me había pasado esto?
- Máscaras faciales de salón de manicura
- Estoy embarazada y estoy pensando en estudiar manicura. ¿Alguna otra preocupación aparte de la ventilación y la higiene, o debería posponerlo por ahora?
- ¿Se debe llevar mascarilla durante todo el servicio?
- ¿Debo desinfectar todos los cepillos de uñas?
- ¿Debo utilizar un "fijador de proteínas" para evitar que se levante?
- ¿Hay que verter el final de una botella vieja en la nueva?
- Algunos productos para uñas afirman que ayudan a fortalecer la placa ungueal. ¿Es válida esta afirmación?
- Algunos de mis clientes sufren picos de calor al endurecer la capa de base y la de acabado.
- ¿armarios con luz ultravioleta para limas de uñas?
- Llevar protector solar, ¿puede provocar una avería en el servicio?
- ¿Cuáles son los requisitos legales para el tratamiento de menores?
- ¿Qué ocurre cuando se mezcla acetona con aceites?
- ¿Qué es la manicura brasileña?
- ¿Qué es una manicura combinada?
- ¿Qué es la manicura rusa?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre limpieza, desinfección y esterilización?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre HEMA y di-HEMA?
- ¿Cuándo caducan los esmaltes de uñas?
- ¿Dónde puedo encontrar niveles seguros de ingredientes para el gel y el gel constructor?
- Why shouldn’t pumice stones be reused in pedicures?
- Show all articles (31) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Acrilatos en los esmaltes de uñas en gel?
- ¿Puede la acetona provocar ampollas?
- ¿Puedo tener dolor de cabeza por trabajar con productos para las uñas?
- Can long-wear nail polishes cause acrylate allergies like gel nails do?
- ¿Puede mi cliente ser alérgico a la acetona?
- ¿Tengo una alergia o una irritación?
- ¿Productos para las uñas sin gluten?
- ¿Cómo he contraído alergia al gel?
- ¿Cómo le explico a mi cliente que "sabe más" que yo que es alérgico?
- ¿Es segura la acetona para eliminar los productos para las uñas?
- ¿Es seguro el BPMMA para clavos a presión?
- ¿Es seguro aplicar un revestimiento sobre la Onicólisis?
- ¿El gel con base de caucho es más propenso a los hongos y las infecciones que el gel normal?
- ¿Existe la manicura de gel segura?
- Uñas presionadas, reacción alérgica curada, ¿puedo volver a probar el gel?
- El aceite del árbol del té, ¿se absorbe a través de la uña?
- Llevar protector solar, ¿puede provocar una avería en el servicio?
- ¿Qué causa la reacción cutánea después de retirar el producto para uñas?
- ¿Qué marcas de gel UV recomiendan?
- ¿Por qué se observan más reacciones de los servicios de esmaltado en gel frente a los servicios de mejora con gel?
- Show all articles (5) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Son mejores las extensiones de uñas de gel que las acrílicas?
- ¿Los geles duros son para todos?
- ¿Mis sistemas de uñas son porosos o no?
- ¿Son las uñas postizas una alternativa segura si tienes una reacción alérgica al gel?
- ¿Son mejores los geles UV para las uñas?
- ¿Se puede utilizar acrílico bajo las puntas de cobertura total?
- ¿Puedo limar la uña natural debajo de una mejora?
- ¿Se pueden mezclar productos Hema y Hema-Free?
- ¿Las uñas de gel estropean las uñas?
- ¿Los pigmentos del esmalte de gel explican por sí solos por qué los profesionales de la manicura lo aplican más fino que el gel de construcción?
- ¿Interrumpe el curado por congelación el proceso de curado?
- ¿El uso de gel UV con puntas transparentes de cobertura total cura correctamente?
- ¿Gel en los dedos de los pies?
- ¿Cómo puedo encontrar una gama de esmaltes en gel UV no tóxicos?
- ¿Es inflamable el esmalte en gel?
- ¿Cuánto producto hay que retirar durante el reequilibrio?
- Si utilizo una lámpara LED para uñas en un producto diseñado para lámparas UV tradicionales, ¿se sobrecurará el gel UV?
- Capa de inhibición y geles no limpiadores
- ¿Es segura la manicura de gel UV para alguien con problemas previos de salud cutánea?
- ¿Es peligroso curar el gel bajo las uñas opacas?
- ¿Es un problema el calentamiento del gel UV?
- ¿Es cierto que el gel LED cura de abajo arriba?
- ¿Es L&P más peligroso que el gel?
- ¿El gel con base de caucho es más propenso a los hongos y las infecciones que el gel normal?
- ¿Es lo mismo una base de caucho que una capa de caucho?
- ¿Existe la manicura de gel segura?
- Sistemas de mezcla de uñas
- Aceite y lifting para uñas
- ¿Practicar conmigo mismo y quitarme fácilmente?
- Uñas presionadas, reacción alérgica curada, ¿puedo volver a probar el gel?
- Retirada del gel poco curado
- ¿Debo comprar mi lámpara de uñas en función de la potencia?
- ¿Debo ponerme uñas de gel o de baño?
- ¿Deben lavarse las manos mis clientes antes de que les aplique el aceite?
- ¿Deben los geles UV "quemar como locos"?
- ¿Hay que quitar la base de goma de la placa de clavos?
- Algunas marcas se astillan más rápido que otras, ¿es un problema del producto o de la química corporal?
- A veces los bordes libres son más claros después del remojo?
- ¿Para rellenar o para empapar?
- ¿Pellizcar o no el realce de la uña?
- Comprender la diferencia entre solución deslizante y limpiador para uñas de poligel
- ¿Utilizar aceite para cutículas durante el remojo?
- GEL UV mezclado con acrílicos - consultas de curado
- Diluyente de esmalte en gel UV
- ¿Qué causa la reacción cutánea después de retirar el producto para uñas?
- ¿Qué significa realmente 'sobreprotegido'?
- ¿Cuál es el método correcto para aplicar un producto de tipo 'BIAB'?
- ¿Qué diferencia hay entre la manicura francesa y la rosa y blanca?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la base de fibra y la base normal?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre HEMA y di-HEMA?
- ¿Qué tipo de productos son las resinas envolventes y los geles no ligeros?
- ¿Qué marcas de gel UV recomiendan?
- ¿Dónde puedo encontrar niveles seguros de ingredientes para el gel y el gel constructor?
- ¿Por qué se observan más reacciones de los servicios de esmaltado en gel frente a los servicios de mejora con gel?
- ¿Por qué se notan las uñas finas después de retirar el esmalte?
- ¿Por qué destiñen algunos colores de gel UV?
- ¿Por qué aconsejan pasar un paño sin limpiar?
- ¿Afectará una lámpara de mesa LED a los geles curados con LED?
- Show all articles (43) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Son seguras las lámparas UV?
- Si utilizo una lámpara LED para uñas en un producto diseñado para lámparas UV tradicionales, ¿se sobrecurará el gel UV?
- ¿Debo comprar mi lámpara de uñas en función de la potencia?
- ¿Qué ocurre con los clientes con antecedentes de cáncer de piel?
- ¿Qué significa realmente 'sobreprotegido'?
- ¿Qué lámpara UV para uñas debo utilizar?
-
- ¡Un greenie! ¿Qué hago? ¿Qué hago?
- ¿Puede la acetona en remojo cambiar la estructura de las uñas?
- ¿Necesitan respirar las uñas?
- ¿La manicura provoca distrofia ungueal media (solenoniquia)?
- ¿Afecta la artritis activa en los nudillos a la placa ungueal en lo que respecta a la elevación?
- ¿Cómo evitar a los "verdes"?
- ¿Cómo eliminar la hiperqueratosis del lecho ungueal?
- ¿Cómo tratar el "síndrome de la uña verde"?
- ¿Cómo afecta el frío a las uñas?
- No tengo claro cómo trabajar las uñas con Pterigión.
- Estoy bastante seguro de que mi cliente de manicura de gel UV tiene OSM.
- ¿Es seguro aplicar un revestimiento sobre la Onicólisis?
- ¿Es el material de los guantes de látex tal que provoca sensibilidad en las manos?
- ¿Leuconiquia o no?
- Liquen plano. ¿Qué debo hacer?
- Should you put gel polish on your skin to check for allergens?
- El aceite del árbol del té, ¿se absorbe a través de la uña?
- La prueba de la onicomicosis (hongos en las uñas) es positiva... ¿Y ahora qué?
- Tratamiento de los hongos en las uñas
- ¿Qué son esas finas líneas negras bajo la uña?
- ¿Qué es la onicolsis?
- What is the best treatment for white keratin granulations on your toes?
- ¿Qué hacer con las uñas enfermas?
- Parches blancos en las uñas después de quitar la pegatina
- ¿Por qué tengo estrías en las uñas?
- Why did my white tips turn yellow and dark right after they were put on?
- Why Do I Get Sinus Irritation at the Nail Salon?
- ¿Por qué la seda o la fibra de vidrio son buenas para las uñas más finas / dañadas y débiles?
- ¿Por qué NO debemos cubrir a los "verdes"?
- Show all articles (14) Colapsar artículos
-
- ¿Aplicar mejoras en las uñas de los niños?
- ¿Cómo puedo salvar una uña cortada?
- ¿Cómo trabajo con un cliente con diabetes de tipo 2?
- Soy autónomo y tengo un salón de belleza a domicilio. ¿Tengo que hacer una evaluación de riesgos?
- ¿Es segura la manicura de gel UV para alguien con problemas previos de salud cutánea?
- Estoy embarazada y estoy pensando en estudiar manicura. ¿Alguna otra preocupación aparte de la ventilación y la higiene, o debería posponerlo por ahora?
- El médico dice "adelante". ¿Lo hago?
- ¿Cuáles son los requisitos legales para el tratamiento de menores?
-
- ¿Puede la acetona en remojo cambiar la estructura de las uñas?
- Can I cut the keratinised proximal nail fold (KPNF)?
- ¿La clienta no deja que nadie le pula las crestas de las uñas?
- ¿Crecen todas las placas ungueales 1 mm a la semana?
- Crecimiento del hiponiquio
- ¿Cuáles son las juntas de la unidad de clavos?
- ¿Qué hace la matriz de la uña?
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre el lecho ungueal y la lámina ungueal?
- ¿Qué es la matriz ungueal?
- ¿De dónde procede la grasa de la lámina ungueal si el lecho ungueal carece de glándulas?
- ¿Dónde está la cutícula?
- ¿Por qué las cutículas de mis clientes se vuelven más gruesas durante el invierno?
-
- ¿Puedo utilizar superglue en lugar de resina para las extensiones de uñas de fibra de vidrio o no funciona igual?
- Can long-wear nail polishes cause acrylate allergies like gel nails do?
- ¿Sabes si remojar las uñas en aceite de aguacate caliente puede mancharlas de amarillo?
- ¿Puede considerarse hipoalergénico un gel que sólo contiene metacrilato de bencilo y dimetacrilato de etilenglicol?
- How does clear 3d sculpting gel work?
- Me confunde el término esmalte híbrido o esmalte de gel híbrido.
- ¿Es seguro el BPMMA para clavos a presión?
- ¿La clienta no deja que nadie le pula las crestas de las uñas?
- ¿Necesitan respirar las uñas?
- ¿La lámina ungueal absorbe las sustancias químicas de los productos que utilizamos?
- ¿Mejoras en los mordedores de uñas?
- ¿Cómo he contraído alergia al gel?
- ¿Es inflamable el esmalte en gel?
- ¿Deben los geles UV "quemar como locos"?
- El aceite del árbol del té, ¿se absorbe a través de la uña?
-
-
Ayuda
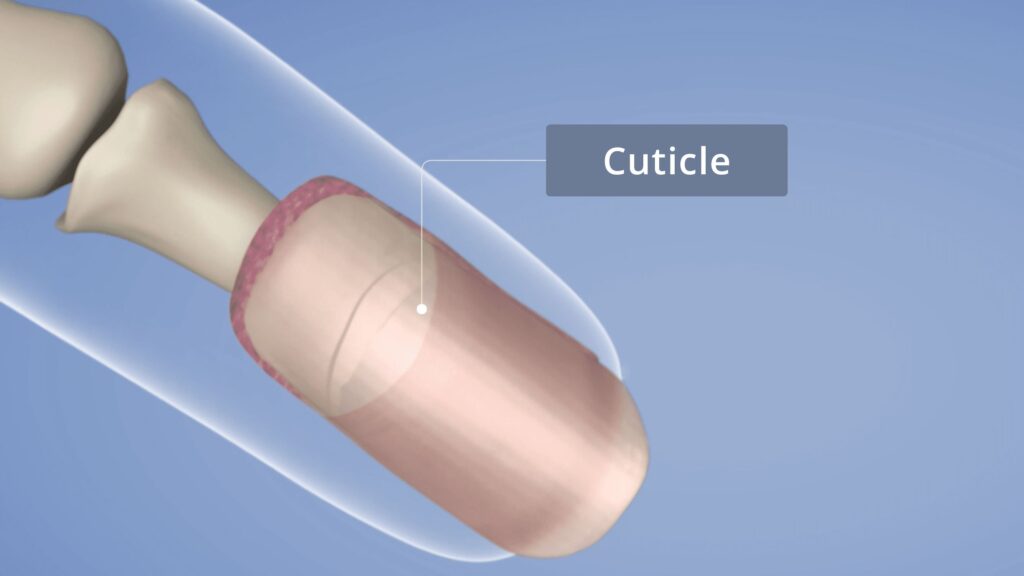
Cuticle
12.6k Visitas
Was this article helpful?
We'd love to hear your feedback:
The cuticle is created by the eponychium on the ventral (on underside) surface of the proximal nail fold. The cuticle is formed of sticky dead skin cells that are shed by the living skin of the PNF just like the skin cells are from any surface of epidermis but instead of falling off in flakes, they are bound together with a very sticky substance, that sticks them firmly to the emerging nail plate beneath them and the frame of keratinised epidermis above them. This important part of the nail seal (or guardian) at the base of the nail is curated by the eponychium which ‘sticks’ the dead skin cells together.
Esta fina capa de piel muerta, se adhiere rápidamente a la placa de la uña y la pliegue ungueal proximal, forming an important seal that protects the important matrix that is behind and below the PNF. This is non-living skin, though, and is safely removed prior to manicures and pedicures, to avoid any lifting of artificial nails, for example.
Pregunte a los expertos
¿Hay que empujar las cutículas hacia atrás?
The answer to this is NO! The cuticle that is exposed and on the nail plate can be safely removed as it is non-living tissue, however to prevent infection of the finger, stop when you reach the frame of keratinised epidermis at the edge of the proximal nail fold. If you go further, and push deep under the proximal nail fold, you open the area up to infection.
En realidad, hay que levantar la cutícula de la lámina ungueal cuando se ablanda y luego retirarla.
¿Cuál es la función de la cutícula?
With the proximal nail fold and the nail plate sealed together with the sticky cuticle in the middle, there is a very efficient first line of defense against all types of invaders from pathogens to chemicals to fungus spores. Any of these that reach the delicate matrix can very easily interrupt the growth of the nail plate and even stop growth altogether.
¿De qué está hecha la cutícula?
La cutícula son células de la piel incoloras y sin vida.
¿Cómo se quita la cutícula?
Lo ideal es que, antes de hacer nada en la cutícula de la uña, ésta se ablande. Históricamente, esto se ha conseguido remojar las uñas en agua ablandada. Esto ablandará la cutícula muy eficazmente PERO también creará un efecto no deseado en la placa de la uña.
The nail plate is hydrophilic, meaning it loves water and is very porous due to the time air spaces within it. If it is soaked in water for 1 minute or more, it will allow water to penetrate the structure, change the shape, temporarily, and make it very soft until the excess water has evaporated. Then it will return to its original shape and regain its hardness.
If an overlay of any kind is applied to a ‘water logged’ nail plate there is a good chance of lifting when the nail returns to its original shape.
Los productos y técnicas modernos se han alejado del remojo en agua y utilizan productos mucho más eficaces para ablandar la cutícula.
These can be an alkaline based product such as sodium hydroxide. This is very efficient at breaking the bonds between dead skin cells and softening the layer. It should, however, NOT be left on the nail nor skin as it will continue to work and will also soften the nail plate and make it very susceptible to damage during the nail service. It needs to be neutralised by a mild solution of soapy water that can be applied via a water spray and drying with a disposable wipe or by washing the hands with liquid soap and running water.
Alternativamente, aplicando una buena aceite de uñas al inicio del servicio, sino después de haber retirado y limpiado las uñas. Esto puede ablandar eficazmente la piel muerta de la cutícula mientras se da forma a las uñas. A continuación, la piel reblandecida puede retirarse de forma segura con una buena herramienta para cutículas, teniendo cuidado de no dañar la superficie de la uña ni el PNF.
This process can also be safely achieved using an e-file. This technique needs education, a slow e-file speed, suitable e-file bit and, preferably oil to minimise any nail plate damage.
There are some e-file techniques that are very extreme in the removal of skin in this area. If you understand the structure and purpose of the PNF it is very clear that this area must be protected at all costs. The ‘seal’ must NOT be broken and therefor opening the matrix to pathogens.
Those nail pros and, indeed, respected educators, who carry out and teach the extreme version of this technique, clearly have no real understanding of the physiology and pathology of the area! (Maybe link to all or any of Vitaly or Doug’s articles on this topic)
En conclusión:
- La cutícula es una fina capa de piel muerta en la superficie de la lámina ungueal.
- Se crea por el eponiquio en la parte inferior del pliegue ungueal proximal.
- The cuticle is the middle layer of the proximal nail fold and nail plate, and it forms a crucial seal at the base of the nail, safeguarding the delicate matrix.
- Puede retirarse de forma segura y eficaz sin dañar la junta.
- Es necesario retirar la cutícula para facilitar la adhesión de las superposiciones a la placa ungueal y conseguir un borde limpio y ordenado en la superposición.
Galería de imágenes
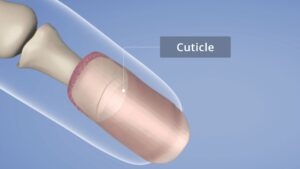
Was this article helpful?
We'd love to hear your feedback:
